Theme:
Euro Antibiotics 2022
Antibiotics conference committee is going to welcome all the participants from all over the world to attain the 3rd Annual Congress on Antibiotics and Bacterial Infections, which is being held in Prague, Czech Republic during October 17-18, 2022. This gathering will give the whole concentration on existing and most recent developments in every aspect of antibiotics and antimicrobial research. In the light of this subject, this opportunity will provide a great platform for discussing among global scientists on antibiotics and its prophylaxis. Therefore, these conference committee members are giving warm welcome all the prominent researchers, students and delegates to participate in this upcoming antibiotics conference event to witness a valuable scientific discussion and to participate in this session for contributing to the future innovations in this field.
Over the years antibiotics have saved many lives by the process of how bacteria were killed using antibiotics. A new study reveals that penicillin and other antibiotics produce destructive molecules that fatally damage bacterial DNA through a long chain of cellular events. New targets involve some bacterial cell is able to save itself from antibiotic-induced DNA damage. Thus recent research is required to understand and solve this problem. In this Conference we invite eminent personalities from universities, clinical research institutions and diagnostic companies, business people oriented with the field of antibiotics to share their research involvements and views on all aspects of this rapidly growing field of antibiotics and thereby, providing a showcase of their latest techniques.
Target Audiences:
- Immunologists
- Pharmacists
- Doctors
- Researchers, academia
- Drug Manufacturers
- Faculties
- Vaccine Associations
- Young researchers
- Occupational Therapists
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Biomedical companies
- Medical and Healthcare Professionals
- Deans and Directors of Medical Universities and Institutes
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Associations of Antibiotics
3rd Annual Congress on Antibiotics and Bacterial Infections is a stage to discuss and learn about the newest developments in the field of Antibiotics, Bacterial infections & Antimicrobial Confrontation as the world’s planning perverse regarding the insistence of new antibiotics as the antimicrobial resistance is growing day by day. Many advanced nations and International health organizations are demanding to focus of the current situation and creation new policies to evade the adverse effects of Antibiotic resistance.
This conference creases researchers, academia, labs, Drug Manufacturers, government agencies, health professionals, hospitals, young investigators, pharma and labs and presents their opinions through key notes, and case study presentations. This conference lays a platform for all the detectives working in the field of Antibiotics, Bacterial infections & Antimicrobial Resistance to know the contemporary developments and the current situation of the conference.
Conference Opportunities
- Speaker Performances
- Poster Display
- Symposium hosting (4-5 member team)
- Workshop organizing
- For Researchers and Faculty Members
For Universities, Associations & Societies:
- Association Partnering
- Collaboration proposals
- Academic Joining
- Assembly Participation
For Students and Research Scholars
- Poster Competition (Winner will get Greatest Poster Award)
- Early Researcher Forum (YRF Award to the best presenter)
- Scholar Attendee
- Assembly Registrations
For Business Delegates
- Speaker Performances
- Symposium hosting
- Book Launch event
- Interacting opportunities
- Listeners participation
For Product Manufacturers
- Exhibitor and Salesperson Booths
- Sponsorships openings
- Product presentation
- Workshop establishing
- Scientific Associating
- Marketing and Networking with customers
Discovery of Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are a kind of antimicrobials used in cure and prevention of bacterial infections. They may prevent or kill the development of bacteria. Numerous antibiotics are also operative against protozoans and fungi; some are toxic to animals and humans also, even when specified in therapeutic dosage.
Pharmacology of Antibiotics:
Antibiotics form part of a broader variety of antimicrobial agents, a group which also includes antifungals, antivirals, antiprotozoal and disinfectants. This group is also known as chemotherapeutic agents. The conference is open for clinical pharmacology of antibiotics, Drug therapy, Pathophysiology, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, Drug screening, classification, synthesis and assays for therapeutic efficacy, Drug disposition, Regulations needed for the approval of antibiotics.
Different Kinds of Antibiotics:
Antibiotics belong to a class of antimicrobials, a longer group which also comprises anti-viral, anti-fungal, and anti-parasitic drugs. The chief classes of antibiotics are beta-lactams which again include penicillin, cephalosporin, macrolides, fluoroquinolone, tetracycline, and aminoglycosides.
Antibiotics for Emerging and Re-Emerging Infections:
Antibiotic-resistant straining of pathogenic bacteria is progressively predominant in hospitals and the public. New antibiotics are desirable to battle these bacterial pathogens, but development in developing them has been slow. The meeting is open to deliberate on synthetic tailoring, discovery of new scaffolds, scheming screens that evade remembering old scaffolds, repurposing libraries of synthetic molecules for use as antibiotics.
The Appearance of Antimicrobial Resistance:
Antibiotic resistance mentions specifically to the resistance to antibiotics that happens in common bacteria that cause infections. Antibiotic resistance is now amongst every part of the world and it’s moving everyone irrespective to the age. When infections develop resistant to first-line drugs, more expensive therapies must be used. To assistance prevent the development of current and future bacterial resistance, it is significant to recommend antibiotics rendering to the principles of antimicrobial stewardship, such as signifying antibiotics only when they are required.
Antibiotics for Several Illnesses and Infections:
Antibiotics are amongst the greatest frequently prescribed medications in modern medicine. Antibiotics are impractical against viral infections.About 2 million Americans each year produce hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), succeeding in 99,000 deaths – the vast mainstream of which are due to antibacterial-resistant pathogens. Two common HAIs alone (sepsis and pneumonia) destroyed nearly 50,000 Americans and cost the U.S. health care scheme more than $8 billion in 2006.
Antimicrobial Confrontation:
Antimicrobial hostility happens when microbes such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites variation for insufficient to antimicrobial drugs such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarial and anthelmintic. Deprived of functioning antimicrobials for reserve and action of infections, medical procedures such as organ transplantation, cancer chemotherapy, diabetes organization and key operation become at very great risk.There have been cumulative public calls for global shared action to address the danger, including an application for international treaty on antimicrobial resistance.
Antibiotic Shortage: A Serious Safety Concern:
Antibiotic lack is of great apprehension to FDA and healthcare community as many of the antibiotics were the sole drugs to treat certain antibiotic-resistant infections for definite infectious conditions.A common repetition during a drug shortage is to choice an alternate therapeutic; however, these agents often present trials and may create safety trepidations. Patient harms including adverse events and medication mistakes may happen. Patients may also file grievances because of drug shortages.
Antibiotics in Various Industries:
Antibiotics requirement is used accordingly in humans and animals because both uses portion to the occurrence, persistence, and growth of resistant bacteria. Food animals play as a basis of resistant pathogens and battle appliances that can directly or indirectly result in antibiotic resistant infections in humans. Sustaining the competence of antibiotic drugs is active to secluding human and animal health.
Micro Organisms in Recent Drug Discovery:
Biodegradable microbes are a prominent source of drug discovery, and numerous microbial products, anti-tumor products, antibiotics, immune suppressants and others are recycled regularly for human therapies. Multidisciplinary way of linking different technologies can assist and reform drug discovery from unproductive microbes and inspect the existing cramp of technologies and situation to swamp such limitations that might further increase the promise of drugs from environmental microbes.
Drug Discovery and Novel Delivery Technologies:
In the previous most drugs have been developed either by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous finding. A new access has been to identify how disease and infection are controlled at the molecular and physiological level and to mark specific entities based on this knowledge. These days, drug delivery corporations are betrothed in the expansion of frequent platform technologies to get ambitious advantage, extend patent life, and growth market share of their products. Formerly a composite has showed its value in these tests; it will begin the process of drug development former to clinical trials.
Antibiotics and Mechanism of Action:
Antibiotics action typically falls within 0ne of 4 mechanisms, three of which contain the inhibition or directive of enzymes involved in cell barrier biosynthesis, nucleic acid metabolism and overhaul, or protein synthesis, correspondingly. Since there is often overlay in these purposes among prokaryotic bacterial cells and eukaryotic mammalian cells, it is not amazing that some antibiotics have also been found to be useful as anticancer agents.
Antibiotics: Market Analysis & Business Opportunities:
The global systemic antibiotics market was respected at $39.6 billion in 2013 and is expected to reach $41.2 billion by 2020, at a CAGR of 0.8%. Since, 2005 this market is seen to produce at an annual rate of 6.6% until 2011. Furthermore, the other antibiotics such as penicillin have 8%, tetracycline 4%, erythromycin 7%, streptomycin 1% and chloramphenicol has 1 % market.
List of Generic Antibiotics and Brand Name Antibiotics:
Amoxicillin, doxycycline, cephalexin, ciprofloxacin, clindamycin, metronidazole,azithromycin,trimethoprim, amoxicillin, evofloxacin. Augmentin, Flagyl, Flagyl ER, Amoxil, Cipro, Keflex, Bactrim, Bactrim DS, Levaquin, Zithromax, Avelox, Cleocin.
Antimicrobial peptides also named Host Defence Peptides are portion of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. AMPs have a broad spectrum of targeted organisms extending from viruses to parasites. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it seems that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form trans membrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as Immunomodulatory.
- Structure and Major Activities of AMPs
- Major Categories of AMPs
- Mechanism of Action of AMPs
- New Targets of AMPs
- Resistance to Antimicrobial Peptides
Antibiotic production and Delivery method:
Antibiotic production can be gathered into three methods: natural fermentation, semi-synthetic, and synthetic. As more and more bacteria endure to grow resistance to currently produced antibiotics, research and development of new antibiotics continues to be important. In addition to survey and development into the manufacture of new antibiotics, repackaging delivery systems is important to improving efficacy of the antibiotics that are currently produced.
- Identifying useful Antibiotics
- Industrial production techniques
- Strains used for the production
- Aerosolization
- Meropenem
Microorganisms Producing Antibiotics:
Antibiotic is one of the most significant commercially exploited secondary metabolites produced by bacteria, fungi and Streptomyces and hired in a wide range. Most of the antibiotics used today are from the microorganisms that live in soil. Bacteria are easy to isolate, culture, maintain and to recover their strain. The main producers of the microbial metabolites, the actinobacteria, fungi and other filamentous bacteria, represent inexhaustible sources for the future.
- Acremonium chrysogenum
- Streptomyces hygroscopicus
- Streptomyces erythreus
- Streptomyces griseus
- Streptomyces aureofaciens
- Streptomyces orientalis
Applications of Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are used commercially, hypothetically useful in medicine for activities other than their antimicrobial action. They are used as antitumor agents, enzyme inhibitors counting powerful hypocholesterolemic agents, immunosuppressive agents, and anti-migraine agents, etc. This session mainly is to focus on the application of anti-bacterials, antifungals, and anti-cancers with their clinical use to date, including the expansion history, side effects, and etc.
- Antitumor antibiotics
- Food preservative antibiotics
- Antibiotics as veterinary medicine
- Antibiotics for control of plant diseases
- Antibiotics as tools in molecular biology
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Antimicrobial drugs:
The pharmacodynamics of an antimicrobial drug narrates its pharmacokinetics to the time course of the antimicrobial effects at the site of the infection. Evidence of the drug's antimicrobial pharmacodynamics properties provides a additional balanced basis for determination of optimal dosing regimens in terms of the dose and the dosing interval than do the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) and minimal bactericidal concentrations (MBCs) resolute in vitro.
- Pharmacokinetics
- Pharmacodynamics
- Antimicrobial susceptibility
- Concentration-dependent antimicrobial activity
- Time-dependent antimicrobial activity
Veterinary Importance of Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are used in livestock production for two simple reasons: disease treatment and disease prevention. Just like humans, animals are prone to bacterial infections. As in hominid medicine, antibiotics are used to commendably delight those infections. In livestock manufacture, antibiotics can also be used to stop disease. There are times in an animal’s life, such as weaning, where definite diseases can be very common. Antibiotics are sometimes used to stop these diseases from becoming established in the first place.
- Aminoglycosides
- Beta Lactam Antibiotics
- Chloramphenicol
- Diaminopyrimidines (Trimethoprim)
- Glycopeptides
Antibiotics for Oncology:
An antibiotic is a chemical made by a microbe that antagonizes the development of other cells. They decrease the viability and clonal expansion of cancer stem cells is of broad importance, as cancer stem cells are increasingly accepted as a distinct cell type that gives rise to therapy resistance, tumour recurrence and detached metastasis. Therapeutic anticancer antibiotics have developed a recognized dealing for definite types of cancer.
- Chemotherapy antibiotics
- Anti-tumour antibiotics
- Cancer Immunotherapy
- Antibiotic prophylaxis
Antibiotics Overuse and Resistance:
Antibiotic higher use is when antibiotics are applied. When they're not needed. Antibiotics are one of the great improvements in medicine. But overprescribing them has controlled to resistant bacteria (bacteria that are tougher to treat). Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria alteration in response to the use of these medicines. Antibiotic resistance occurs naturally, but misappropriation of antibiotics in humans and animals is accelerating the process. Antibiotic resistance leads to extended hospital vacations, higher medical costs and improved mortality.
- Overuse and overprescribing of antibiotics
- Antibiotic resistance
- Superbugs and Super resistance
- Risks of antibiotic over usage
- Prevention and control
Antibiotic-resistant Bacterial infections:
Antibiotics have been used to treat people with infectious diseases produced by bacteria. Though, definite antibiotics have been used so extensively and for so extended that some bacteria that cause disease have develop resistant to them, making these treatments less actual. Antibiotic resistance happens when the medicine mislays its ability to destroy bacteria. As a result, the organisms continue to produce and cause infection, even in the occurrence of the antibiotic.
- Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria
- Multidrug-resistant bacteria
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae
- Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae
Genetics of Antibiotic Resistance:
Developed bacterial antibiotic confrontation can consequence from the mutation of usual cellular genes, the attainment of distant resistance genes, or a combination of these two mechanisms. The feast of mobile genetic rudiments such as plasmids, transposons, and integrons has importantly donated to the fast dissemination of antimicrobial resistance amongst several bacterial types of human and veterinary prominence.
- Antibiotic resistance genes
- Horizontal genetic transfers
- Multidrug-resistant genes
- Resistance-nodulation-division
- β-lactamases
Clinical Trials of Antibiotics:
There has been a growing use of antibiotics in all areas of medicine. Clinical trials to examination antibiotics are generally of a fewer than satisfactory quality. The main objective of original clinical trials, at least, is to provide the pharmaceutical company with adequate information to persuade the regulatory authority that the drug is effective, safe and well produced.
- Factors in the Designing the antibiotics
- Genomic screening and information technology
- Randomized clinical trials
- Phases of clinical trials
- Interpretation of the clinical trials
- Drug Evaluation
Clinical and Economic Burden of Antibiotic Resistance:
Evidence of the scientific and financial inspiration of antimicrobial resistance is valuable to affect programs and performance in healthcare facilities, to guide policy makers and subsidy agencies, to describe the forecast of individual patients and to rouse interest in emerging novel antimicrobial agents and therapies. This conference primarily emphasis on selection of significant matters that necessity be measured when designing or interpreting studies of the clinical and economic outcomes related with antimicrobial resistance.
- Antibiotic Resistance
- Economic Analysis
- Healthcare associated infections
- Outcomes
- Study design
New antibiotics and non-antibiotic approaches:
New antibiotics essential to be established, which surgeons will be able to use when existing drugs no extended work. Non-antibiotic treatments can also decrease our requirement on antibiotics. The government inspires corporations to advance new drugs and treatments. New technologies can also help prevent infections.
- Research collaboration on antibiotic resistance
- Development of new antibiotics
- Non-antibiotic approaches
- New health technologies
Current research in antibiotic resistance:
Antibiotic overuse and misuse has managed to an increasing number of bacteria in humans, animals and the environment that are resilient to life-saving antimicrobial therapies.Research comprises epidemiology of together Gram-negative and Gram-positive infections, genetic mechanisms of resistance, expansion and broadcast in the hospice setting, as well as the public, and antimicrobial stewardship.
- Novel antibacterial drug discovery
- Investigating antibiotic use
- Determining minimal-risk policies
- Nutrition as a method of controlling bacterial infections
- Economic implications of bacterial resistance
The Next Generation Approach of Antibiotics:
As research into antibiotic resistance enlarges, it is important to accept an openly proactive approach to antibiotic resistance identification and investigation, as well as antibiotic therapy development. This practical approach involves using a combination of functional met genomics, next-generation sequencing and cutting-edge computational methods to monitor the evolution and dissemination of resistance before a given resistance because emerges in a pathogen or in the clinical setting, as well as proactively developing next-generation therapies that target these resistance determinants.
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
- Functional met genomics
- Cutting-edge computational methods
- Next-generation surveillance
- Next-generation therapeutics
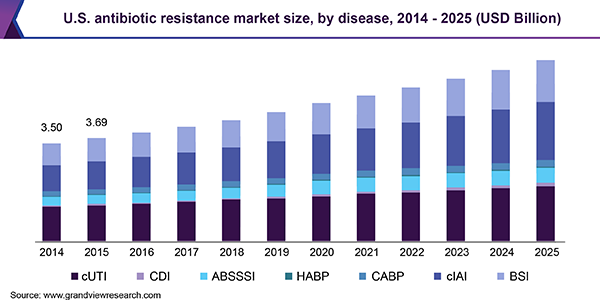
The worldwide Antibiotics market is valued at $6,727.29 million in 2014 and is relied upon to develop at a CAGR of 13.03% in the vicinity of 2014 and 2019. Expanding sickness weight of irresistible maladies and expanded subsidizing for social insurance consumption are the vital development drivers for this market amid the conjecture time frame. The pharmaceuticals request piece characterized the major share 0f the Antimicrobials advertise in 2014; while the sustenance claim portion is normal develop at the most bewildering CAGR in the neighbourhood of 2014 and 2019 in the universal Antibiotics cabinet. The worldwide scientific antimicrobials marketplace is predictable to spread USD 5.77 Billion by 2021 from USD 3.35 Billion in 2016, rising at a CAGR of 11.5% from 2016 to 2021. Market growth can be attributed to issues such as the technical progressions; rising occurrence of catching diseases and rising eruption of epidemics; increasing healthcare outflow across the world; and accumulative funding, research grants, and public-private savings in the field of life science researches.
Evolving regions such as Asia-Pacific (including Japan, China, and India) are predictable to develop the new revenue-generating compartments in the marketplace in the next five years. The Asia-Pacific market is projected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period owing to the growing number of hospitals and clinical diagnostic laboratories in India and China, escalating research competences for the progress of ground-breaking and reasonable clinical Antibiotics testing procedures across India, China, and Japan; and increasing occurrences of infectious diseases.
Market Research:
Market research is vital to the development of the industrial market, and endures to be in demand. In 2018, we anticipate delivery of new editions of our report on Antimicrobials Testing in the Global emission.
Global Market Survey:
Antimicrobials scope was esteemed at over USD 24.3 billion in 2017 and will exceed USD 675.2 billion with 7.9% CAGR from 2017 to 2024. At Worldwide Market It is a sole blend of main and subordinate research, with validation and iterations, in order to minimalize nonconformity and current the most precise examination of the manufacturing.
Increasing mandate of new technologies will drive the biotechnology industry size. we’ve seen wonderful development and alteration in the industrial diagnostics industry, mainly in the food safety sector expertise in all aspects of the market, desirable wide experience in business organization, strategy development and global business, Antibiotics test volumes, marketplace standards and methods used by food creators about the world, based on full interviews with more than 450 food production amenities in America, Europe and Asia, including Japan. Total test capacities have increased 128%, and testing for specific foodborne pathogens like Salmonella and E. coli grew at an even earlier rate.
The worldwide DNA sequencing market is predictable to reach USD 85.5 Million by 2025 from USD 310.1 Million in 2017 growing at a CAGR of 8.5% during the prediction period.
The global market for Food Antibiotics reached nearly $7.1 billion in 2017. This market is expected to grow to nearly $9.6 billion in 2017 and $15.7 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2017 to 2025.
Global Nanotechnology Market was esteemed at $216.2 billion in 2017 and $448.3 billion in 2017. The total market is expected to grow at a compound annual development rate (CAGR) of 19.3% from 2017 through 2025 and reach $828 billion by 2025.
Product:
Based on knowledge, the industry is segmented keen on tissue engineering besides regeneration, fermentation, PCR, nanotechnology, chromatography, DNA sequencing and cell based assay. In 2017, the tissue engineering and regeneration division accounted for maximum income and was cherished at over USD 11.3 billion. However, the nanotechnology, fermentation and cell based assay subdivisions will information moneymaking development owed to increasing R&D enterprises by frequent biotechnological and pharmaceutical companies.
The global clinical Antimicrobials market is respected at $6,727.29 million in 2014 and is predictable to grow at a CAGR of 13.03% between 2014 and 2019. Accumulative disease burden of infectious diseases and increased funding for healthcare expenditure are the vital growth drivers for this market during the forecast period. The pharmaceuticals submission partition accounted for the principal ration of the Antibiotics marketplace in 2014, whereas the food solicitation segment is expected produce at the maximum CAGR amongst 2014 and 2019 in the worldwide Antimicrobials marketplace.
Market Overview:
Numerous microorganisms are used in industrial Antibiotics, comprising laboratory-selected mutants, naturally occurring organisms, and hereditarily modified organisms (GMOs). Antimicrobials research and development is finding cumulative application in oil and gas administrations, the food and beverage industry, and environmental testing organizations.
In addition, the traditional R&D in the biopharmaceutical industry is seeing an upsurge, due to drug development research, which is plateful in the growth of the industrial Antibiotics market.
Increased request for nutraceuticals and other fermented merchandises further drives the importance of industrial application of Antimicrobials on a great scale. Such influences are obliging to determination the industrial marketplace.
However, in the market, there are numerous conflicts experiential regarding the practice of genetically modified organisms in food sources, which are expected to limit the development of the industrial Antibiotics market.
Conference Highlights
- Discovery of Antibiotics
- Pharmacology of Antibiotics
- Different Kinds of Antibiotics
- Antibiotics for Emerging and Re-Emerging Infections
- The Appearance of Antimicrobial Resistance
- Antibiotics for Several Illnesses and Infections
- Antimicrobial Confrontation:
- Antibiotic Shortage: A Serious Safety Concern
- Antibiotics in Various Industries
- Micro Organisms in Recent Drug Discovery
- Drug Discovery and Novel Delivery Technologies
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | October 17-18, 2022 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Infectious Diseases and Treatment
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy
- Annals of Infections and Antibiotics
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by












